Utilizziamo i cookie per rendere migliore la tua esperienza di navigazione. Per rispettare la nuova direttiva sulla privacy, è necessario chiedere il tuo consenso per impostare i cookie. Per saperne di più.
Basic concepts of embOS-MPU embOS-MPU offers memory protection on top of the proven real-time operating system embOS. It significantly enhances both stability and safety of your embedded applications and thereby simplifies any certification process. The operating system and all tasks deemed privileged are memory protected and isolated from any ill effects of unprivileged tasks. Due to a fully compatible API, existing embOS applications may be adapted to embOS-MPU with minimal effort. embOS-MPU can be used in any application from battery-powered, single chip products to systems demanding ultra-fast response, flexibility and multiple tasks. Typical fields include, but are not limited to medical equipment, automation, avionics, and further safety-critical applications.
SEGGER embOS-MPU - Introduction
What is Memory Protection?
Memory protection is a prevalent mechanism to control memory access rights and is part of most modern processor architectures and operating systems. The main purpose of memory protection is to avert specific tasks from accessing memory that has not been allocated to them, thus preventing possible bugs or even malware contained in one task from affecting the entire system.
In order to achieve this, application tasks that could possibly affect other tasks or the OS itself must be restricted from accessing the whole memory, special function registers and the OS's control structures. For example, tasks that execute third-party code may be considered unsafe and should be restricted accordingly. Such application tasks must not run on the same privilege state as the OS, which runs in fully privileged mode and has access to all memory, peripheral and CPU features. Instead, these tasks must run in unprivileged state and have restricted access to specific memory locations only.
What is embOS-MPU?
embOS-MPU uses the hardware's memory protection unit as well as additional software mechanisms implemented with embOS-MPU to prevent one task from affecting the entirety of the system. This guarantees that even in case a bug occurs in one task, all other tasks and the operating system itself continue execution.
With embOS-MPU, all privileged tasks have full access to the whole memory. An unprivileged task, however, has specific access permissions to each distinct memory region. In order to access peripherals, additional memory locations and OS control structures, device drivers as well as specific embOS API may be called from within an unprivileged task.
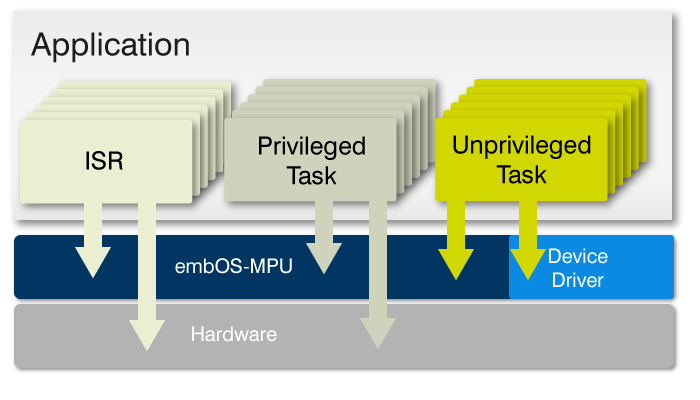
An application based on embOS-MPU therefore consists of two distinct parts
- The first part runs in privileged state: It initializes the MPU settings and includes the device drivers. This part contains critical code and must be verified for full reliability.
- The second part is the application itself, which does not need to be verified for full reliability. As it runs in unprivileged state, this part cannot affect the complete system.
Working with Unprivileged Tasks
By default, a newly created unprivileged task has read access to RAM and ROM, but may execute code in ROM only, while write access is restricted to its own task stack. In order to access peripherals, additional memory locations and OS control structures, device drivers as well as specific embOS API may be called from within an unprivileged task.
ACCESS TO PERIPHERALS
An unprivileged task may be granted access to additional memory regions, e.g. when a task needs to write LCD data to a framebuffer in RAM and a device driver is deemed inefficient for this purpose. Access permissions are fully configurable in regards to read access, write access and code execution.
MPU VIOLATION MANAGEMENT
In case an unprivileged task violates its access restrictions or triggers a fault exception by other means, it is automatically terminated and an optional user callback function is executed to notify the application about this. This callback may also perform further actions in regards to that task, e.g. restarting the complete system.
- Suitable for any safety-critical application
- Available for any MCU containing a hardware MPU or MMU
- Unlimited number of privileged und unprivileged tasks possible
- Unprivileged tasks 100% Sandboxed
- Simple and straightforward runtime configuration
- Easy to integrate in both new and existing products
Non esitare a metterti in contatto con i nostri esperti.
Basta chiedere qui








